Introduction
Website backups are a crucial part of website management, yet they are often overlooked until disaster strikes. Whether it’s a cyberattack, accidental data loss, or a server crash, having a reliable backup ensures that you can quickly restore your website with minimal downtime.
In this guide, we’ll explore the best practices for backing up your website regularly, helping you protect your data and keep your site running smoothly.
Why Regular Website Backups Are Essential

A website is a valuable digital asset that requires protection against unexpected failures. Without a backup, you risk losing crucial data, including blog posts, customer information, and design customizations. Regular backups help you:
- Recover lost data due to accidental deletion or software errors.
- Protect against cyberattacks like ransomware and malware.
- Restore your website quickly after a crash or server failure.
- Ensure business continuity by minimizing downtime.
By implementing a robust backup strategy, you can prevent costly disruptions and maintain a reliable online presence.
1. Choose the Right Backup Solution
Selecting the right backup method depends on your website’s platform, hosting provider, and business needs. The most common backup options include:
A. Hosting Provider Backups
Most hosting providers offer built-in backup solutions, often included in their hosting plans. These automated backups provide an easy recovery option in case of failure.
Best for: Beginners and small businesses relying on managed hosting services.
B. Manual Backups
For full control over your backups, you can manually export your website’s files and database. While this method requires effort, it ensures that you have a local copy of your site.
Best for: Advanced users who want extra security and custom backup options.
C. Backup Plugins & Software
Many Content Management Systems (CMS), like WordPress, offer backup plugins that automate and schedule backups. Some popular options include: UpdraftPlus (WordPress plugin), BackupBuddy and Jetpack Backup.
Best for: WordPress users and businesses looking for automated backup solutions.
D. Cloud-Based Backup Services
Cloud backup solutions, such as Google Drive, Dropbox, or Amazon S3, provide secure storage for your website’s backup files. This option prevents data loss due to local device failure.
Best for: Businesses needing off-site backups for extra security.
2. Schedule Automated Backups
Relying on manual backups is risky because human error can lead to missed backups. Instead, set up automated backups to ensure consistency.
Best Practices for Backup Frequency:
- Daily backups for e-commerce sites, news websites, or high-traffic platforms.
- Weekly backups for small business websites or personal blogs with moderate updates.
- Monthly backups for static websites with minimal content updates.
Setting up a recurring backup schedule guarantees that you always have a recent version of your website available for recovery.
3. Store Backups in Multiple Locations
Storing backups in only one location is risky—if that location fails, your backup is useless. To ensure data safety, follow the 3-2-1 backup rule:
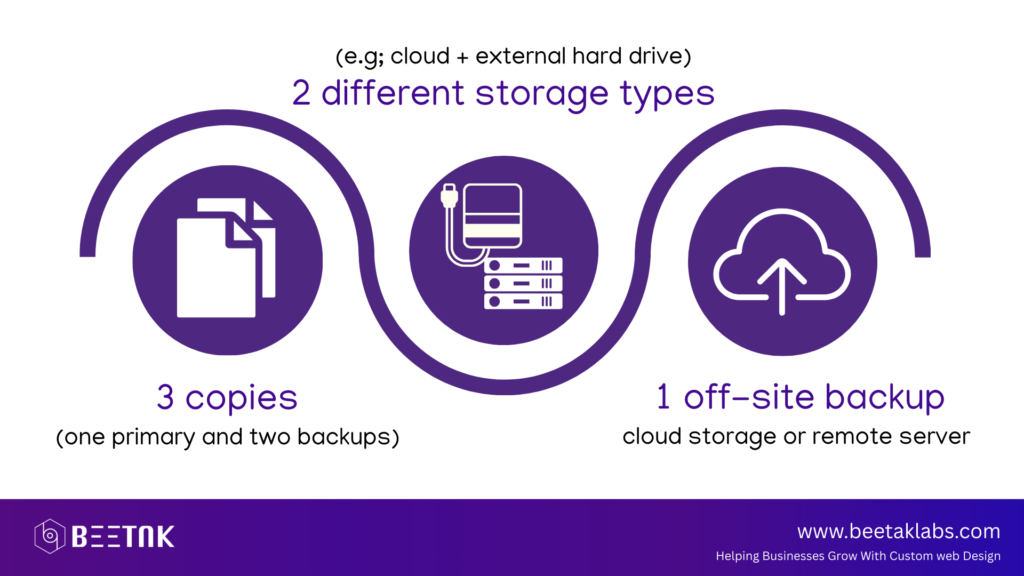
Recommended Backup Storage Options:
- Local Storage – Save a copy on an external hard drive or local server.
- Cloud Storage – Use services like Google Drive, Dropbox, or Amazon S3.
- Remote Server – Store backups on a different server or hosting provider
By keeping redundant copies of your website’s backup, you minimize the risk of losing data permanently.
4. Back Up Both Files and Databases
A complete website backup includes both website files and databases:
- Website Files: Includes images, themes, plugins, and scripts.
- Database: Stores all website content, including posts, user data, and settings.
When using cPanel, WordPress plugins, or hosting backup tools, ensure that both files and databases are included in the backup process.
5. Test Your Backups Regularly
A backup is useless if it’s corrupt or incomplete. To ensure that your backups are functional:
Test Your Backup by:
- Restoring it to a staging environment (test site).
- Checking for missing files or errors after restoration.
- Verifying that all database records are intact.
Testing backups quarterly ensures that you can restore your website without issues in case of an emergency.
6. Encrypt and Secure Your Backups
Hackers often target backup files because they contain sensitive information. To enhance security:
- Use encryption tools to protect backups stored in the cloud.
- Set up password protection for backup files.
- Restrict access permissions to only authorized users.
Many backup services and plugins offer built-in encryption features, ensuring that your backups remain safe from unauthorized access.
7. Create a Disaster Recovery Plan
Even with regular backups, you need a clear strategy for restoring your website quickly in case of an emergency. Your disaster recovery plan should include:
- Step-by-step instructions on how to restore backups.
- Contact information for your hosting provider or technical support team.
- A list of login credentials needed to access backup storage.
Having a structured recovery plan minimizes downtime and allows for a smooth website restoration process.
Final Thoughts: Protect Your Website with Regular Backups
Website backups are your first line of defense against cyber threats, accidental data loss, and server failures. By implementing automated, secure, and redundant backups, you can ensure your website remains protected and operational at all times.
Start backing up your website today, and safeguard your business from unexpected failures. A well-maintained backup strategy will save time, money, and stress in the long run.


